Petty cash funds are classified as cash because these funds are used to meet current operating expenses and to pay current liabilities as they come due. Even though petty cash has been set aside for a particular purpose, its balance is not material, so it is included in the cash balance in the financial statements. Cash shortages are recorded in a separate income statement expense account usually known as the cash short or over account. Most cash short and over is classified as a retailers’ accounting systems have a cash over short account setup because they generally deal with cash sales everyday. To safeguard against cash handling errors and misappropriation, businesses implement internal controls that serve as a framework for financial integrity.
Cash Over and Short Journal Entry

This transparency is not merely a matter of regulatory compliance but also a testament to the company’s commitment to financial accuracy. Auditors examine these reports to understand the frequency and magnitude of discrepancies, which can serve as indicators of the effectiveness of current internal controls. They may also provide recommendations for enhancing procedures to mitigate future occurrences.
Start with Petty Cash
- A series of cash overs and shorts may be a sign of theft or other problems in the company.
- On the other hand, if its balance is on the credit side, it will be presented as miscellaneous revenue instead.
- U.S. agency securities, certificates of deposit and time deposits, commercial paper, corporate debt securities, and other asset classes as well.
- The term cash over and short refers to an expense account that is used to report overages and shortages to an imprest account such as petty cash.
- However, in bankruptcy proceedings bondholders are at least well positioned to be paid back.
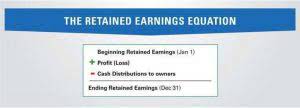
This is because cash and cash equivalents are current assets, meaning they’re the most liquid of short-term assets. A firm should note instances of cash variances in a single, easily accessible account. This cash-over-short account should be classified as an income-statement account, not an expense account because the recorded errors can increase or decrease a company’s profits on https://www.instagram.com/bookstime_inc its income statement. On the other hand, if the company has a cash shortage in the petty cash fund, it can make the journal entry with the debit of cash over and short account instead.

Cash over and short journal entry
In the example, if your https://www.bookstime.com/ petty cash account’s original balance was $1,000, subtract $550 from $1,000 to get $450, which is the amount by which you need to replenish the account. The cash over and short account is used when an imprest account, such as petty cash, fails to prove out. The account is typically left open until the end of a company’s fiscal year, when it is then closed and reported as a miscellaneous expense on the income statement. The culmination of diligent cash management practices is often reflected in the audit process. When auditors assess a company’s financial records, cash over and short instances must be transparently reported.

A controller conducts a monthly review of a petty cash box that should contain a standard cash balance of $200. He finds that the box contains $45 of cash and $135 of receipts, which totals only $180. This cash shortfall is recorded as a debit to the cash over and short account (which is an expense) and a credit to the petty cash or cash account (which is an asset reduction). Cash equivalents are short-term, highly liquid assets that can readily be converted into known amounts of cash and with little risk of price fluctuations. An example of a short-term cash equivalent asset would be one that matures in three months or less from the acquisition date. They may be considered as “near-cash,” but are not treated as cash because they can include a penalty to convert back to cash before they mature.
- Cash is the most liquid of the financial assets and is the standard medium of exchange for most business transactions.
- Alternatively, if there had been too much cash in the petty cash box (a rare condition indeed!), the entry would be reversed, with a debit to cash and a credit to the cash over and short account.
- The journal entry for this sale would debit cash for $96, credit sales for $95, and credit cash over short for $1.
- These materials were downloaded from PwC’s Viewpoint (viewpoint.pwc.com) under license.